Clay-Fly Ash Burnt Bricks: An Experimental Study
The production of burnt bricks is an essential part of the construction industry, and it has been a traditional practice for centuries. However, the process of brick-making has a significant environmental impact due to the high energy consumption and carbon emissions associated with it. In recent years, researchers have been exploring alternative materials and methods to reduce the environmental impact of brick-making. One such material is fly ash, which is a byproduct of coal combustion in thermal power plants.
An experimental study on Clay-Fly Ash Burnt Bricks was conducted by Jayant L. Patil and Dr. Arun Kumar Dwivedi to investigate the properties of bricks made from clay and fly ash. The study aimed to determine the optimal proportion of fly ash that can be used in brick-making without compromising its strength and durability.
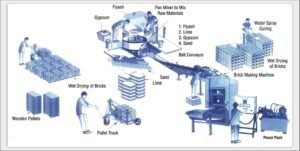
The fly ash used in the study was collected from the Thermal Power Station (Eklahre) in Nashik, Maharashtra. The clay used was locally sourced from Nashik as well. The bricks were made using a hydraulic press machine with varying proportions of clay and fly ash ranging from 0% to 75% fly ash content.
The experimental setup involved preparing samples of bricks with different proportions of clay and fly ash, followed by testing their physical properties such as compressive strength, water absorption capacity, density, and porosity. The results showed that as the proportion of fly ash increased in the mixture, there was a decrease in compressive strength but an increase in water absorption capacity.
The compressive strength values ranged from 3.5 MPa for 0% fly ash content to 2 MPa for 75% fly ash content. Similarly, water absorption capacity increased from 10% for 0% fly ash content to 20% for 75% fly ash content. However, the density of the bricks decreased from 16938.36 N/m3 for 0% fly ash to 13811.88 N/m3 for 75% fly ash.
The study concluded that the optimal proportion of fly ash in clay-fly ash burnt bricks is around 25-30%. This proportion provides a balance between compressive strength, water absorption capacity, and density. The use of fly ash in brick-making has several advantages, including reducing the environmental impact of brick production by utilizing a waste material and reducing the amount of clay required for brick-making.
In addition to its environmental benefits, using fly ash in brick-making can also lead to cost savings due to the lower fuel consumption required for firing the bricks. The study cited an Austrian company, “Wienerberger Porotherm,” which has reported a 60% energy saving compared to conventional methods.
Furthermore, the use of fly ash in brick-making can help minimize the problem of waste disposal. Fly ash is a byproduct of coal combustion and is typically disposed of in landfills, which can have negative environmental impacts. By using fly ash in brick-making, this waste material can be repurposed and diverted from landfills.
The study’s findings have significant implications for the construction industry, particularly in developing countries where burnt bricks are still widely used. The use of fly ash in brick-making can help reduce the environmental impact of construction activities while also providing cost savings and waste reduction benefits.
However, it is important to note that the study was conducted under controlled laboratory conditions and may not reflect real-world scenarios. Further research is needed to determine the feasibility and practicality of using fly ash in brick-making on a larger scale.
Conclusion:
The experimental study on Clay-Fly Ash Burnt Bricks conducted by Jayant L. Patil and Dr. Arun Kumar Dwivedi provides valuable insights into the properties of bricks made from clay and fly ash. The study highlights the potential benefits of using fly ash in brick-making, including reducing environmental impact, cost savings, and waste reduction. However, further research is needed to determine the optimal proportion of fly ash for different types of clay and real-world scenarios.